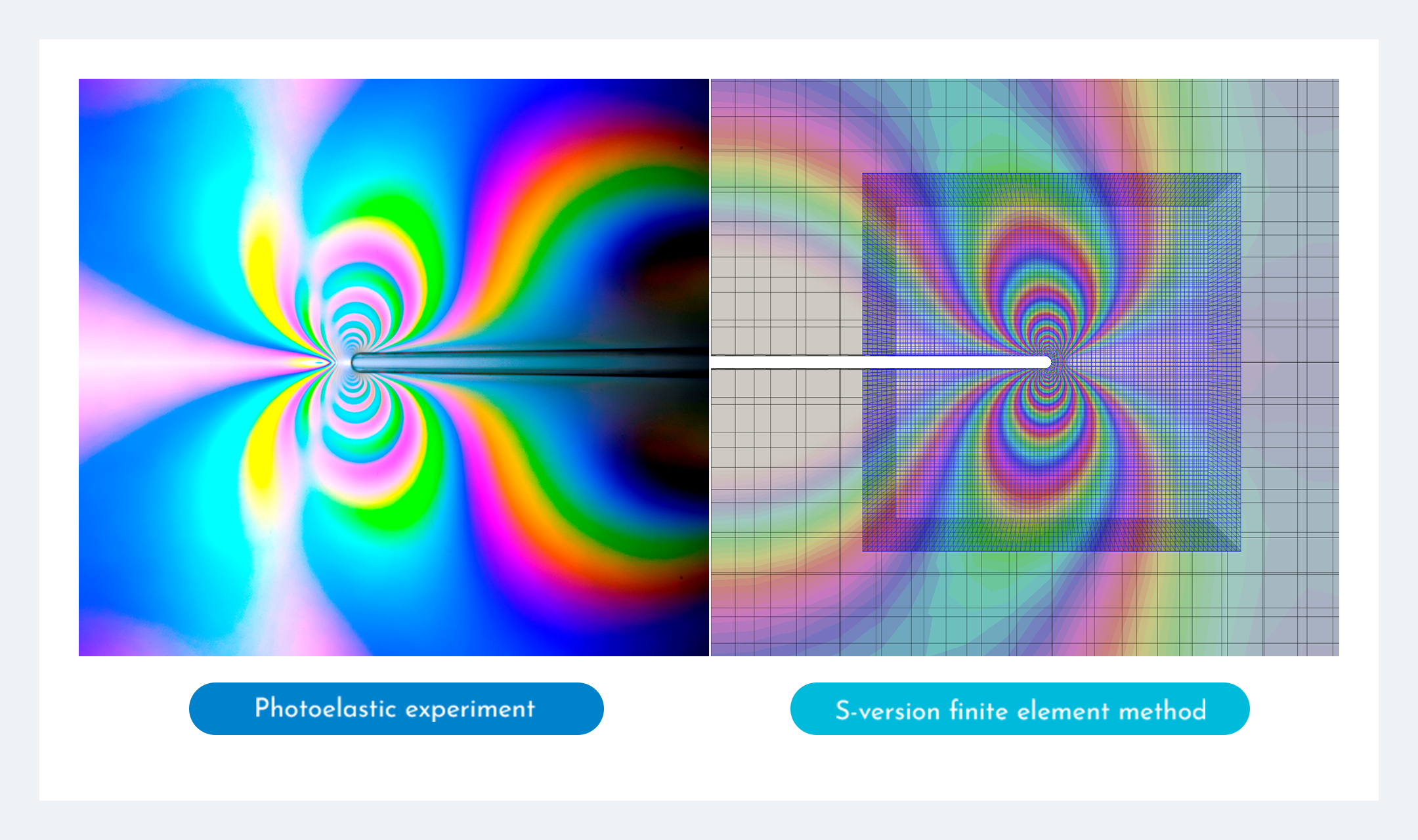

Kazuki Shibanuma’s Laboratory,
The University of Tokyo
Fracture Mechanics
& Structural Integrity
Why Study
Fracture Mechanics?
Understanding and preventing fractures in materials and structures has been a hot topic since the early days of human civilization. Fracture phenomena are closely linked to building and device safety. Therefore, predicting and controlling such fractures is essential not only for designing high-performance novel materials and structures but also for minimizing the risk to human lives.


Today, fracture mechanics is an active area of study in engineering, and knowledge in this field is highly valued by the industry. Our group seeks to develop innovative methods and strategies to understand fracture phenomena better. The extremely complex physical processes underlying fracture hold answers to fundamental engineering questions like “How can we create fracture-resistant materials?” and “How can we use a given material or component without causing it to fracture?”


Publications
| No. | Authors | Title | Journal | Volume (Year), Pages | Categories |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 84 | Fuminori Yanagimoto Tianyu He Kazuki Shibanuma* |
The state-of-art in studies on brittle crack arrest in steel |
Beyond FEM
Verification
Validation
Brittle fracture
Crack arrest
Fracture criterion
|
||
| 83 | Tianyu He Naoki Morita Naoto Mitsume Fuminori Yanagimoto Katsuyuki Suzuki Yun-Jae Kim Kazuki Shibanuma* |
Beyond FEM
Validation
Brittle fracture
Crack arrest
Fracture criterion
In-situ observation
|
|||
| 82 | Yutaro Abe Daisuke Fukui Ryota Nagashima Nobuo Nakada* Kazuki Shibanuma |
Beyond FEM
Validation
Brittle fracture
Fracture criterion
Material characterisation
|
Awards
| No. | Winner(s) | Title | Organisation | Month, Year |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 34 | Kazuki Shibanuma |
Outstanding Presentation Award |
Japan Society for Computational Engineering and Science (JSCES) | Sep. 2024 |
| 33 | Kazuki Shibanuma |
Outstanding Presentation Award |
JSMS Committee on Multiscale Materials Mechanics | Jun. 2024 |
| 32 | Tianyu He |
Dean’s Award (Best Master Thesis of Department) |
School of Engineering, The University of Tokyo | Mar. 2024 |
Gallery




Access
Department of Systems
Innovation,
School of Engineering,
The University of Tokyo
7-3-1 Hongo, Bunkyo-ku, Tokyo, 113-8656, JAPAN
Eng. Bldg. No. 3, Hongo Campus, The University of Tokyo
Associate Professor: Room 334
Laboratory Office: Room 348
7 min walk from Nezu Station (Chiyoda Line)
8 min walk from Todaimae Station (Namboku Line)
13 min walk from Hongo-sanchome Station (Marunouchi Line and Oedo Line)
Contact
Feel free to contact us if you are
interested in
joining our group or
conducting collaborative research.